The Role Of Ethical Hacking In Cybersecurity
Introduction to Ethical Hacking
To introduce ethical hacking, let us first understand the terms that make up the word. We all know what ethical means in a general sense. If not, then you should know that it refers to something that is legitimate and in accordance with the rules and standards of society. Now, "hacking" is the term that most people misinterpret. Hacking simply means tinkering with the mechanism of an object to make it work for our needs, and a person who performs such an activity is a hacker.
HACKER noun 1. A person who enjoys learning the details of computer systems and how to stretch their capabilities--as opposed to most users if computers, who prefer to learn only the minimum amount necessary. 2. One who programs enthusiastically or who enjoys programming rather than just theorizing about programming.
Why the special term? To tweak something, you need to know how it works. It's rare to find people who know how to work with software. If you do, you can make new programs or change existing ones. This is called "hacking," and it's a compliment. The person who does it is a "hacker."
Now you know what ethical hacking means. It means hacking with permission. Some hackers do it for wrong reasons without permission. They are called "black hat hackers" or "unethical hackers." We use "hacking" when we mean it in a good way. We use "cracking" when we mean "hacking" in a bad way.
Types of Hackers
- As per working
- White Hat Hackers
- Black Hat Hackers
- Grey Hat Hackers
- Hacktivists
- State Sponsored Hackers
- Suicide Hackers
- As per knowledge
- Script Kiddies
- Admins
- Coders
Intent, History and Cause
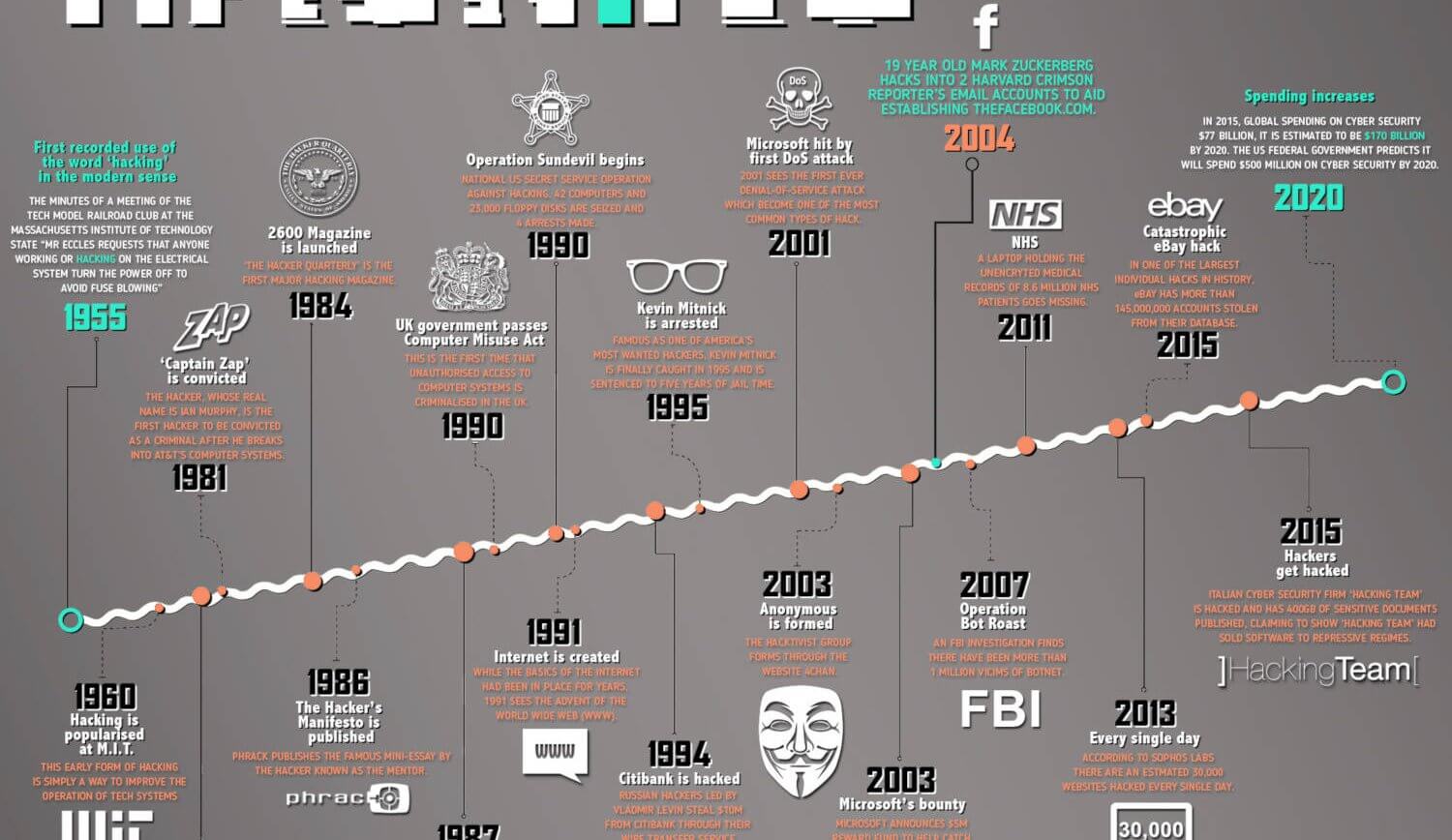
Let's go back to when computers and the internet first became available to everyone. As people started using computers in new ways, their popularity and prices rose. Computers were first used in universities for research. Because of this, the access was fairly restricted. When refused access to computers, some users would challenge the use access controls that had been put in place. They would steal on passwords or account numbers by looking over some-one's shoulder, explore the system for bugs that might get them past the rules, or even take control of the whole system. They would do these things in order to be able to run the programs of their choice, or just to change the limitations under which their programs were running.
At first, these computer intrusions were harmless. The worst thing that happened was the theft of computer time. Sometimes, these recreations were practical jokes. However, they didn't stay benign for long. Sometimes, the less talented or careful intruders would accidentally damage a system, and the system administrators would have to restart it or make repairs. Other times, when these intruders were caught, they would react with destructive actions.
When the number of these destructive computer intrusions became noticeable, due to the visibility of the system or the extent of the damage inflicted, it became "news", and the news media picked up on the story. Instead of using the more accurate term "computer criminal", the media began using the term "hacker" to describe individuals who break into computers for fun, revenge, or profit. Since calling someone a "hacker" was originally meant as a compliment, computer security professionals prefer to use the term "cracker" or "intruder" for hackers who turn to the dark side of hacking. For clarity, we will use the explicit terms "ethical hacker" and "criminal hacker" for the rest of this article.
Why Ethical Hacking Is Important in Cybersecurity
The technology of internet of things is growing at rapid rate. Things are getting connected to internet and the only way to secure them is keeping secret password for each. You or the users feel once they have set a strong password, they are completely secured whereas they are unaware of the darker part of internet. People with intentions to hurt, steal or harm in any of the way constitute the darker part of this web. We have mentioned what such people are referred to as in the above sections - "crackers". So, here comes the role of Ethical Hacker, the good ones.
To stay secure from getting cracked most basic strategy would be to learn to think like a criminal hacker. How the criminal hacker would carry out cracking, what tools and techniques are used by them. An ethical hacker does the same. He/she knows how a cracker can intrude into his/her system, so all the existing vulnerabilities in his/her system are scanned and removed.
A user study by Garfinkel and Miller, states that many users may still be vulnerable in spite of having strong passwords. The future is life bounded in internet hence, security is the most important factor to be taken care of. This is why people should invest in and learn ethical hacking. As the fundamental philosophy behind protection of every system is the same, be it a computer of an individual or a business, the only thing that differs between the two is the investment and learning done.
I will list some points out for why businesses would invest in ethical hacking and same correspond to that of an individual too only if one could open their eyes and put in the work.
- Prevent Data Breaches: Identifying vulnerabilities reduces the risk of data breaches.
- Strengthen Security Posture: Ethical hacking helps organizations understand their weaknesses and take corrective actions.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Many industries require regular security assessments and ethical hacking practices to comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
- Building Trust: A proactive security strategy builds customer and partner confidence by demonstrating a commitment to safeguarding data.
Common Techniques and Tests Used by Ethical Hackers
There are several kinds of testing that I will mention below. Any combination of them may be called for:
- Remote network: This test simulates the intruder launching an attack across the Internet. The primary defenses that must be defeated here are border firewalls, filtering routers, and Web servers.
- Remote dial-up network: This test simulates the intruder launching an attack against the client's modem pools. The primary defenses that must be defeated here are user authentication schemes. These kinds of tests should be coordinated with the local telephone company.
- Local network: This test simulates an employee or other authorized person who has a legal connection to the organization's network. The primary defenses that must be defeated here are intranet firewalls, internal Web servers, server security measures, and e-mail systems.
- Stolen laptop computer: In this test, the laptop computer of a key employee, such as an upper-level manager or strategist, is taken by client without warning and given to the ethical hackers. They examine the computer for passwords stored in dial-up software, corporate information assets, personnel information, and the like. Since many busy users will store their passwords on their machine, it is common for the ethical hackers to be able to use this laptop computer to dial into the corporate intranet with the owner's full privileges.
- Social engineering: This test evaluates the target organization's staff as to whether it would leak information to someone. A typical example of this would be an intruder calling the organization's computer help line and asking for the external telephone numbers of the modem pool. Defending against this kind of attack is the hardest, because people and personalities are involved. Most people are basically helpful, so it seems harmless to tell someone who appears lost where the computer room is located, or to let someone into the building who "forgot" his or her badge. The only defense against this is to raise security awareness.
- Physical entry: This test acts out a physical penetration of the organization's building. Special arrangements must be made for this, since security guards or police could become involved if the ethical hackers fail to avoid detection. Once inside the building, it is important that the tester not be detected. One technique is for the tester to carry a document with the target company's logo on it. Such a document could be found by digging through trash cans before the ethical hack or by casually picking up a document from a trash can or desk once the tester is inside. The primary defenses here are a strong security policy, security guards, access controls and monitoring, and security awareness.
Each of these kinds of testing can be performed from three perspectives: as a total outsider, a "semi-out sider", or a valid user.
A total outsider has very limited knowledge about the target systems. The only information used is available through public sources on the Internet. This test represents the most commonly perceived threat. A well-defended system should not allow this kind of intruder to do anything.
A semi-outsider has limited access to one or more of the organization's computers or networks. This tests scenarios such as a bank allowing its depositors to use special software and a modem to access information about their accounts. A well-defended system should only allow this kind of intruder to access his or her own account information.
A valid user has valid access to at least some of the organization's computers and networks. This tests whether or not insiders with some access can extend that access beyond what has been prescribed. A well defended system should allow an insider to access only the areas and resources that the system administrator has assigned to the insider.
The Ethical Hacking Process
I'll start by explaining how a cracker operates to help you protect yourself. There's more to it than this, but this is the basic process any hacker will use to access your system.
To learn defense by offence, stage the hack on your own devices. Learn each stage in detail and take your time. Remember that patience is key.
After successfully executing each stage, go to the next, repeat the same and keep building on top of each other. Also learning the concepts of hacking and applying them for securing any system or for any good cause is what defines Ethical Hacking.
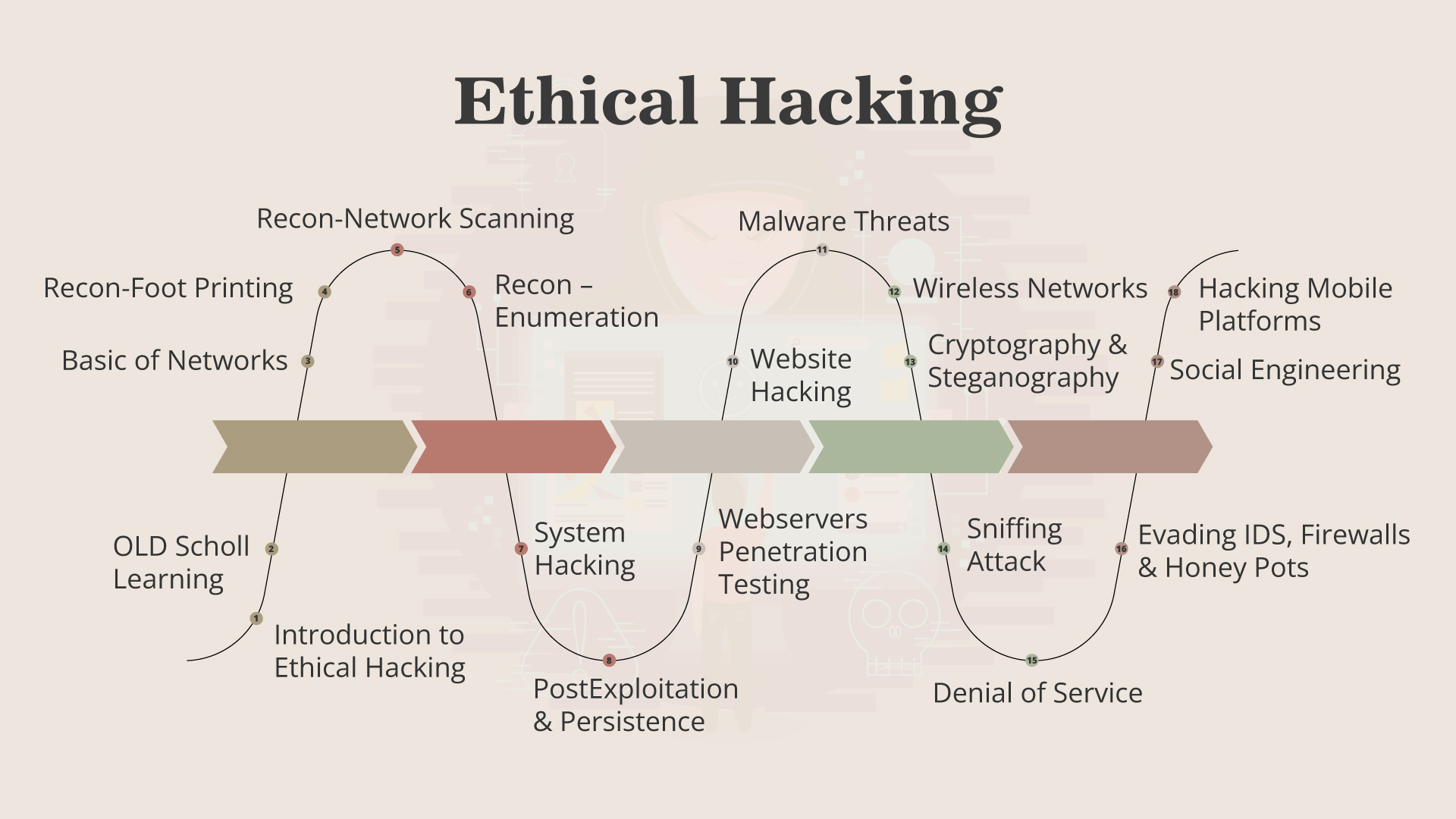
There are five stages that hackers go through to get the job done.
- Reconnaissance
- Scanning and Enumeration
- Gaining Access
- Maintaining Access
- Clearing Tracks
-
Reconnaissance:
Reconnaissance is a set of processes and techniques used to secretly discover and collect information about a target system. This is also known as "foot printing" or in short referred to as "recon".
During reconnaissance, an ethical hacker attempts to collect as much information about a target system as possible, following the seven steps listed below -
- Gather preliminary information
- Identifying active machines
- Determine open ports and access points
- OS fingerprinting
- Reveal all the services on ports
- Network mapping
-
Scanning and Enumeration:
The second step of ethical hacking and penetration testing involves two terms that is scanning and enumeration.Scanning is a common technique used by a pen-tester to discover open doors. Scanning is used to find out the vulnerabilities in the services running on a port. During this process you have to find out the alive host, operating systems involved, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, servers/services, perimeter devices, routing and general network topology (physical layout of the network), that are a part of the target organization.
There are again three types of scanning: -
Port Scanning
Includes the entire overview of scanning as we discussed above. In short, the term port scanning is mainly used to find out the vulnerabilities and weak points in the port that is used in the network. -
Network Scanning
In network scanning, we identify all active hosts which are present on a network. During this procedure we will come to know about IP addresses of individual host. -
Vulnerability Scanning
In vulnerability scanning we will come to know about the operating system/s installed on a target machine and enumerate it to gather details like its version or any service pack if installed to find out weaknesses and vulnerabilities and try to use it as an access point to try and break into the system. -
Gaining Access
Once the reconnaissance is done and all the vulnerabilities are scanned, the hacker then tries to gain the access with the help of certain tools and techniques by exploiting those weak points and vulnerabilities.You can learn the execution of this stage by yourself. I will point to some resources to get started. But you would by now think by yourself what happens in this stage by the name itself. So, apart from your primal understanding I want to point out that the outcome of this stage may not necessarily align with its name and so can be revelated in either of the following two ways. -
Truly breaking in and gaining master access to the system in order retrieve passwords, install spyware, damage the system by deleting its root files and programs or any such activities.
-
Damaging the system or network without breaking in and gaining access to it. Some famous examples for it would be performing denial-of-service (DoS)/distributed denial-of-service attacks(D-DoS). The intentions behind such an action would mostly be void of any actual or justifiable purpose and would breed on top of anarchy, insensitivity and chaos. Yes, the company would tight fit itself and design, manage its networks to defend against these kinds of attacks but never they are entirely un-affected.
-
Maintaining Access
Once an attacker has gained the access of the targeted system, he/she can exploit both the system and its resources and furthermore use the system as a launch pad to scan and harm other systems, or he/she can keep a low profile and continue exploiting the system without actual user noticing all these acts. Both these actions can destroy the organization leading to a catastrophe. Rootkits gain access at the operating system level while a Trojan horse gains access at the application level. Attackers can use Trojan horses to transfer usernames, passwords, and even credit card information stored on the system.
Organization can use intrusion detection systems or deploy honeypots to detect intruders. The latter though is not recommended unless the organization has the required security professionals to leverage the concept of protection. -
Clearing Tracks
An attacker needs to destroy evidence of his presence and activities for several reasons like evading detection and further punishment for the intrusion. Erasing evidence often known as "clearing tracks" is a requirement for any attacker who wants to remain obscure and evade trace back. This step usually starts by erasing the contaminated logins or any other possible error messages that may have been generated on the victim's system from the attack process.It is really very crucial for invaders to make the system look like it as the same before they gained access and established backdoors for their use. Any files, which have been modified or altered, need to be changed back to their original attributes or format.For example, a buffer overflow attack usually leaves a message in system logs which needs to be cleared. Next, attention is turned to affecting changes so that future logins are not logged.An attacker can use the system as a cover to launch fresh attacks against other systems or use it as a means of getting into another system on the network without being detected. Thus, this phase of attack can turn into a new cycle of attack by using the five stages all over again.
Tools Of the Trade for Ethical Hackers
The hack is about using the right tools in the right way. We call them "tools," but they're just programs written by hackers or professionals who know more about the system than you or I. If you remember, in the introduction section A hacker is someone who knows a lot about a particular software or mechanism and can quickly create new programs to demonstrate how to break into it. They create new programs, which we use as tools. It's about finding the right tools, understanding what they do, how to use them and using them correctly.
Here are some tools that were used in each stage. You can research more and find other tools. I couldn't mention them all, but I gave you some ideas. Look for tools that work like the ones I mentioned. This will help you know what to look for.
| Tool | OS | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Supported by all | Gives all the basic information available regarding the website | |
| Whois Lookup | Gnu/Linux, Windows and MacOS(using website), Fedora | lookup tool allows you to search for domain name availability and all the information of the host such as ownership info, IP address history, traffic, etc. |
| NSLookup | WindowsOS, MacOS, Gnu/Linux, Solaris | A network utility program used to obtain information regarding Internet servers. As the name suggests, the utility finds all the name server information for the domains by querying the Domain Name System (DNS) |
| Tool | OS | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Ping | AIX, Gnu/Linux, Windows, HP-UX, Solaris, MacOS, SunOS | used to check that the host computer which the user is trying to locate is alive and can accept the requests |
| Tracert | MacOS, Windows, Gnu/Linux, FreeBSD, WindowsNT | a network diagnostic tool used to determine the path the packet has taken from one IP to other |
| Nmap | Gnu/Linux, Microsoft Windows, OpenBSD, Solaris, IRIX, Mac OSX, HP-UX, SunOS | Nmap is an abbreviation of 'Network Mapper' and is a well-known free open-source hackers' tool. Nmap is mainly used for network discovery and security auditing |
| Zenmap | Gnu/Linux, Microsoft Windows, OpenBSD, Solaris, IRIX, Mac OSX, HP-UX, Sun OS | There is a GUI version of Nmap called "Zenmap" used for the network diagnostics |
| Nikto Website Vulnerability Scanner | AIX, Gnu/Linux, Windows, HP-UX, Solaris, MacOS, SunOS | Nikto is an open source (GPL) web server scanner which is able to scan and detect web servers for vulnerabilities |
| Netcraft | Ubuntu, Fedora, Solaris | Netcraft provides internet security services including anti-fraud and anti-phishing services, application testing using the analysis of the network |
| Tool | OS | Description |
|---|---|---|
| John The Ripper | Unix, Windows, DOS, MacOS, OpenVMS | John the Ripper, mostly referred to as "John" is a popular password cracking penetration testing tool that is most commonly used to carry out dictionary attacks |
| Wireshark | Linux, MacOS, BSD, Solaris, Microsoft Windows | Wireshark efficiently captures data packets in a network in real time and then displays the data about the packets travelling in human-readable format |
| KonBoot | Gnu/Linux, MacOS, BSD, Solaris, Microsoft Windows | Kon-Boot is a software utility that allows users to bypass Microsoft Windows passwords and Apple macOS passwords without lasting or persistent changes to system on which it is executed. |
| pwdump7 | Microsoft Windows | Pwdump7 is the program that yields the LM and NTLM password hashes of local user accounts from the Security Account Manager (SAM) |
| Aircrack | MacOS, Unix, Gnu/Linux, OpenBSD, HP-UX | Aircrack is one of the most popular wireless passwords cracking tools which you can use for 802.11a/b/g WEP and WPA cracking. Aircrack uses the best algorithms to recover wireless passwords by capturing packets |
| Fluxion | All Linux and Gnu/Linux Distributions | Fluxion is the future- a blend of technical and social engineering automation that tricks the victim into handing over the Wi-fi password to the attacker in a matter of keystrokes |
| Cain and Abel | Microsoft Windows | Cain and Abel is a tool to recover (i.e. "crack") many types of passwords using methods such as network packet sniffing and by using the tool to crack password hashes |
| Tool | OS | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Metasploit Penetration Testing Software | Ubuntu, Windows, Redhat, MacOS | Metasploit is a cyber security framework that provides the user with vital information regarding known vulnerabilities and helps to formulate penetration testing plans, strategies and methodologies for exploitation |
| Beast | Microsoft Windows | Beast is an example of trojan horse used to create backdoors, more commonly known in the hacking community as a Remote Administration Tool or a "RAT" |
| Cain and Abel | Microsoft Windows | Cain and Abel is a tool to recover many types of passwords using methods such as network packet sniffing and by means of the tool to crack password hashes |
| Tool | OS | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Metasploit Penetration Testing Software | Ubuntu, WindowsOS, Redhat, MacOS | Metasploit is a cybersecurity framework that provides the user with vital information regarding known security vulnerabilities and helps to formulate penetration testing plans, strategies and methodologies for exploitation |
| OSForensics | Windows | Forensic took to delete the log files and registry files |
Getting Started as An Ethical Hacker
You can learn what happens behind the scenes. This knowledge is useless unless you do something with it. If you can pass your time by replicating and reproducing any of the above stages, you can do it as a hobby. And you will learn a lot. You will understand how things work better than you did before.
If you want to get serious about it or make it a career, you need more than just experimentation. You have the tools, but you don't know how they work or why.
You still lack the philosophy, methodology and mechanism of the tools you are using. You should know about how the software works. There are many factors involved. I will point out the aspects you should focus on to work as an ethical hacker.
- Skills Required: Knowledge of operating systems, networking, programming, and security concepts. Read and read...read a lot. Collect yourself some textbooks, articles, academic papers, journals, whatever material you might find and keep yourself thorough. I am afraid that there is no shortcut.
- Certifications: Certifications like CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker), OSCP (Offensive Security Certified Professional), and CompTIA PenTest+ are valuable for credibility and career growth. If you are just acquiring knowledge for yourself, they are not mandatory but if you want work as a professional in a company or organization, they are a must.
- Hands-on Practice: Use platforms like Hack The Box, TryHackMe, and PentesterLab to build practical skills in a controlled environment. The above mentioned are remote services meaning they are online. You can either install a virtual machine in your system and download boxes from Vulnhub, run it from the virtual machine and now you can practice locally.
- Stay Updated: Cybersecurity is constantly evolving; staying current with the latest threats, tools, and technologies is vital. And that is how you can get an edge over criminal hackers.
Ethical Considerations and Legalities
This article is about ethical hacking, not criminal hacking. We must remember to stay on the right side of the line between good and bad. It's easy to deceive yourself and not realize you're doing something wrong. The hardest thing for an ethical hacker is to maintain the integrity of the line. What is the line? It starts with your consciousness.
- Obtain Proper Authorization: Always get written permission before testing any system.
- Follow a Code of Ethics: Adhere to the professional code of conduct, such as the EC-Council's Code of Ethics.
- Understand Local Laws: Different countries have varying laws around hacking and cybersecurity; ensure you’re compliant with the legal framework in your jurisdiction.
Conclusion, Next Steps and Final Words
You know about ethical hacking and cybersecurity. What now? Is this all you need to know? Not at all! You need to do more than read theory. You also need to learn by doing. How do you do it? Use your phone, computer or other device to experiment. Don't be afraid. If you make a mistake, you might lose your data. Back up your work before you try anything new. Do it so you understand how it's done and how to defend against it. If you don't know how an attack is done, you can't set up an effective defense.
I hope you protect yourself against anything bad that's coming your way. There is.
References
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/5386933
- Meenakshi N. Munjal
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8391982
Recommendations
Stay vigilant!
Wishing you a good hack!
As always,
Venu Kotamraju ;-)
.png)



That was a insight blog. The author did a thorough reasearch.
ReplyDelete